A router is a hand tool that routs (or gouges out) an area in a hard material such as wood or plastic. Instead of routing by hand, a CNC router uses computer numerical control (hence the name), giving makers accuracy and precision only a machine could achieve. Let’s break down the components most CNC routers have in common:
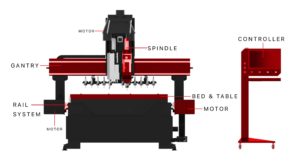
THE BRAINS: Computer System and Controller
It starts with your CAD/CAM software, such as KDC, which turns your vision into a digital design and translates them into a G-code program of instructions for the machine.
The Computer System:
– Creates and sends digital instruction or G-code
– Converts G-code into a 2D or 3D item ready to be cut
– Adapts and controls the axes system.
• X – front to back
• Y – left to right
• Z – up and down
– Controls operations such as desired direction, cutting speed, and changing tooling bits. It can also control vacuum zoning, component marking & printing, loading and unloading, depending on extended features available in your machine.
The computer system is operated using a mix of Controller devices such computer screens, keyboards, cameras, and handheld remotes.

PRO TIP: Get 5th Generation (5G) CNC with its own dedicated system and controller for each machine, a touch screen interface, and screen over 20” for faster processing and ease of use for the operator.
The Body:

Cutting Bed & Table
• Holds and secures materials in place. Clamps, fasteners, vacuum, and adhesives are often used for workholding.
• Table sizes can be customized according to production needs. Usually, more space than necessary is better than a cramped one.
• Table tops can come in different configurations (vacuum, T-slot, perforated, disposable), depending on work requirements. These affect the way materials are secured and how dust is extracted.

The Gantry
• Straddles the bed and keeps the spindle’s movements steady. A solid gantry helps minimize vibrations during cutting. Some machines have tools attached to the gantry for faster tool changes.
PRO TIP: Get 5G CNC with:
• Table loading and unloading upgrade capabilities that eliminate heavy lifting.
• A high-flow, intelligent vacuum system & pump for stronger hold down and assisted cleaning that doesn’t interrupt production.
The Legs: The Linear Drive Systems
The controller says go and the legs take off. The Linear Drive System converts controlled rotary motion to controlled linear motion. It’s what moves the gantry and the spindle in a directed axis.
– The Motor
CNC motors commonly use either stepper or servo motors. Stepper motors are smaller and inexpensive and are used for low speed, acceleration & accuracy requirements. Servo motors are more sophisticated, run faster and are more accurate.
– Linear Rail System
It guides the path of movement along axes while supporting secondary load and machine components. Depending on the size or complexity of the CNC, the rail may use ball bearings or rack and pinion. A properly functioning rail system is firmly affixed in place and allows the right amount of friction for the machine to travel freely .

PRO TIP: Get 5G CNC that uses servo motors and rack & pinion on the X & Y axes instead of rubber belts or ball screws. Rubber belts slack and stretch after repeated use, causing backlash and requiring constant retensioning.
The Muscle – Spindle
Powered by electricity or compressed air, the spindle holds the tool and rotates it on an axis. It’s the part that does the cutting. Torque, speed, horsepower, and bearing system are important specs to evaluate. Heat and contaminants are what wears it out the fastest.

PRO TIP: Get 5G CNC air-cooled spindles plus drill bits that have great warranty/exchange programs since they take a lot of beating.
The basic mechanics of these components are essentially the same across machines and change little over the years. To a great extent, they determine what you can produce, how fast you do it, and how well the quality is. As long as these parts are in good, serviceable condition, they should do the job they are meant to do.
However, as your needs may change from the time you buy your machine, you should be mindful of how your machine can expand to fit any future upgrades you might need.
For more Pro Tips & 5G CNC:
7 Questions to Ask When Getting Your 1st CNC Router
Video link: https://youtu.be/SnHzP_z36Z0
Check out our 5G CNC
Meet the Fully-Loaded, Battle-worthy Python XPR
Video link: https://youtu.be/wx8C-I7gXec







